By Dr Biju Krishnan BDS FICD FCGDent
The landscape of orthodontic care is undergoing a revolutionary transformation. While traditional orthodontics has long concentrated on achieving straight teeth and correcting bite relationships, an emerging paradigm advocates for a more comprehensive, integrative methodology that extends beyond dental alignment to address fundamental functional issues affecting growth, health, and overall wellbeing. This represents the core philosophy of holistic orthodontics.
For paediatric patients particularly, the developmental years present an invaluable opportunity for intervention. Treatments that guide optimal craniofacial development, enhance airway function, and support healthy oral habits can yield profound long-term benefits that extend well into adulthood.
For paediatric patients particularly, the developmental years present an invaluable opportunity for intervention. Treatments that guide optimal craniofacial development, enhance airway function, and support healthy oral habits can yield profound long-term benefits that extend well into adulthood.
This comprehensive examination explores the essential components of an integrative approach to orthodontic care in young patients, emphasising tongue posture and function, airway development, nasal breathing optimisation, craniofacial growth guidance, myofunctional therapy, cranial osteopathic support, and the pioneering work of the Society for Dentofacial Growth and Function (SDGF).
The Foundation of Holistic Orthodontic Philosophy
When adopting a comprehensive, whole-body perspective, orthodontics transcends being defined by any single appliance or technique. Instead, it embodies a philosophy of care that recognises the interconnected nature of teeth, jaws, airway, posture, breathing patterns, and overall health. The fundamental objective shifts from purely cosmetic tooth alignment to restoring and supporting normal physiological function.
This approach acknowledges that dental crowding and malocclusion frequently represent symptoms of underlying functional imbalances, including poor tongue posture, chronic mouth breathing, or disrupted craniofacial growth patterns. By addressing these root causes particularly during a childs formative developmental years, practitioners can achieve more stable and healthier long-term outcomes.
Understanding Systemic Dysfunction in Craniofacial Development
In biological systems, dysfunction refers to unpredictable changes that arise from disruptions in normal physiological function. Within the context of craniofacial growth, factors such as mouth breathing, low tongue posture, and compromised muscle tone introduce chaotic elements that can redirect natural growth trajectories away from optimal patterns.
These disruptions may commonly manifest as:
- Crowded or misaligned teeth
- Compromised facial aesthetics and balance
- Restricted airway development
- Sleep disordered breathing patterns
- Functional disorders including temporomandibular dysfunction
Rather than viewing these issues as isolated problems, holistic orthodontic approaches treat them as interconnected symptoms of broader systemic imbalance, focusing treatment efforts on restoring normal function and establishing proper balance throughout the craniofacial complex.
The Critical Importance of Airway Development and Nasal Breathing
One of the most significant paradigm shifts in holistic orthodontics involves the emphasis on airway development and nasal breathing patterns. Proper nasal breathing serves as the foundation for healthy facial growth and optimal systemic health throughout life.
Why Airway Health Matters
Facial Growth Patterns: Chronic mouth breathing fundamentally alters tongue posture, leading to high, narrow palatal development, retruded jaw positioning, and characteristic longface growth patterns that can affect both function and aesthetics.
Functional Impact: A compromised airway significantly affects sleep quality, cognitive function, behavioural patterns, and general health outcomes, creating cascading effects throughout multiple body systems.
Malocclusion Development: The tongue is a major driving force for jaw development (see below). As described above, restricted nasal airways contribute to incorrect tongue resting position and incorrect tongue function such as poor swallowing patterns. This affects the tongue’s ability to optimise jaw development which in turn can lead to jaws which are smaller, shorter or narrower than normal which in turn can exacerbate dental crowding and bite problems.
Sleep Disordered Breathing: Conditions including snoring, upper airway resistance syndrome, and paediatric obstructive sleep apnoea often stem from underdeveloped jaws and compromised airway dimensions.
Nasal breathing provides numerous physiological advantages, including the ability to filter, warm, and humidify inhaled air while stimulating nitric oxide production that enhances oxygen uptake. Additionally, proper nasal breathing encourages correct tongue posture against the palate, which naturally supports proper arch development and facial balance.
An holistic orthodontic approach places strong emphasis on identifying and correcting mouth breathing patterns early in development, often requiring collaboration with ENT specialists, myofunctional therapists, and other allied health professionals to address underlying causes and establish healthy breathing habits.
Tongue Function: The Architect of Facial Development
It is functions of the facial muscles and the tongue which ultimately determine facial form. While genetics provides the basic developmental blueprint, function serves as the primary determinant of final outcomes. The tongue plays a particularly pivotal role in shaping the maxilla (upper jaw) and influencing overall facial development patterns.
Optimal Tongue Posture Characteristics
- Gentle resting position against the roof of the mouth
- Maintenance of proper lip seal supporting nasal breathing
- Provision of natural expansive forces that develop broad, Ushaped dental arches
Consequences of Dysfunctional Tongue Posture
- Development of narrow, high vaulted palates
- Dental crowding and malocclusion patterns
- Reduced nasal airway space
- Functional difficulties with speech, swallowing, and chewing
Myofunctional therapy is frequently prescribed to retrain proper tongue posture and function, restore correct swallowing patterns, and support optimal nasal breathing habits.
Craniofacial Growth: Maximising Developmental Opportunities
A child’s facial structures and jaws represent dynamic, responsive systems rather than static anatomical features. Proper nasal breathing, optimal tongue posture, and functional chewing patterns are essential for harmonious growth and development.
Growth Pattern Disruptions and Their Effects
In growing children, facial development ideally progresses forward and outward, allowing for proper jaw alignment, adequate airway space, and balanced facial proportions. Disruptions in these natural growth patterns can lead to significant adverse effects:
- Vertical growth tendencies associated with mouth breathing, potentially leading to longface syndrome and open bite conditions
- Transverse deficiencies resulting in narrow arches and crossbite relationships
- Sagittal discrepancies, including retruded maxilla and mandible positioning, affecting facial profile and airway dimensions
A holistic orthodontic approach aims to guide craniofacial growth through functional correction techniques, minimizing the need for tooth extractions or surgical interventions later in life while optimising natural developmental potential.
Comprehensive Treatment Modalities in Integrated Orthodontic Care
Adopting a holistic perspective on orthodontic care in children typically involves combining multiple interventions to address the complete range of functional and developmental needs.
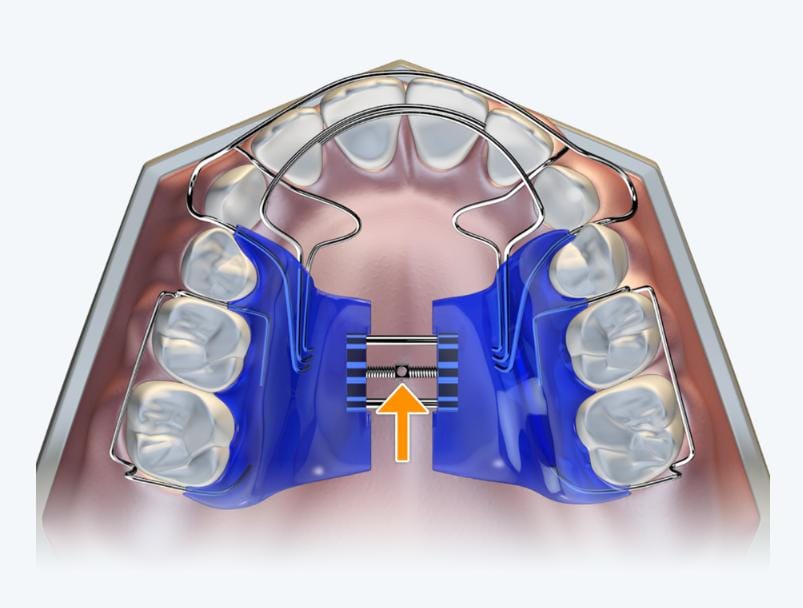
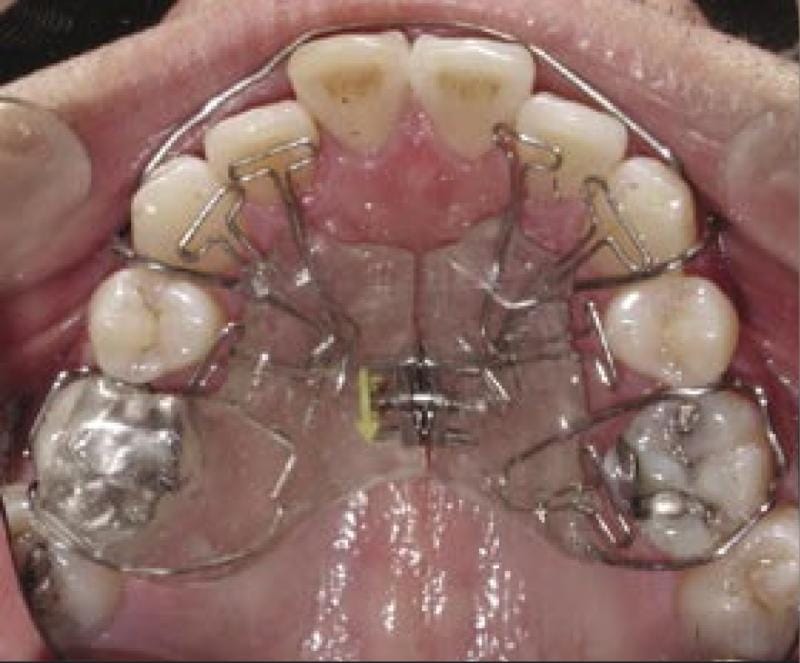
- Functional Orthopaedic Appliances
Functional orthopaedic appliances serve as central components in holistic orthodontic treatment by addressing root causes of malocclusion, including underdeveloped jaws, poor oral posture, and compromised airway space. Unlike traditional braces that primarily focus on dental alignment, these appliances guide jaw growth and correct functional imbalances during crucial developmental periods.
Primary goals include:
- Stimulating natural forward and lateral jaw growth
- Correcting dysfunctional habits including mouth breathing and tongue thrusting
- Increasing airway volume to support better nasal breathing
- Creating stable foundations for future dental alignment
When utilised during active growth phases, functional appliances influence not only dental positioning but can also provide far reaching benefits for facial aesthetics, airway health, and overall craniofacial function.
- Myofunctional Therapy Integration
Myofunctional therapy represents an exercise-based treatment approach that focuses on improving strength, coordination, and proper function of the tongue, lips, cheeks, and facial muscles. This therapy specifically targets correction of habits like mouth breathing, tongue thrusting, and incorrect swallowing patterns that can significantly affect jaw development and bite alignment.
- Breathing Retraining Programs
Restoring nasal breathing as the default respiratory mode represents a cornerstone of holistic orthodontic treatment. Many children develop compensatory mouth breathing due to factors including enlarged adenoids, allergies, chronic nasal congestion, or simply poor habit formation. While seemingly harmless, persistent mouth breathing carries significant implications for craniofacial development, dental health, and overall wellbeing.
- Cranial Osteopathic Support
Cranial osteopathy provides gentle, handson therapy that focuses on releasing tensions within cranial bones, sutures, and fascial systems. While subtle in application, these techniques can significantly impact craniofacial development and overall function.
During growth periods, restrictions or asymmetries in cranial structures, whether from birth trauma, posture, or functional imbalances can influence facial and jaw development patterns. Tightness or strain in these areas may impede optimal growth, contributing to jaw asymmetry, bite issues, and airway restrictions.
Cranial osteopathy is frequently used in conjunction with functional orthodontic treatments, helping create a more responsive and balanced environment for optimal growth and development.
- Lifestyle and Habit Modification
When embracing a holistic orthodontic perspective, correcting malocclusion extends beyond appliances and exercises to encompass everyday habits and lifestyle factors that significantly influence craniofacial development.
Dietary Considerations: Modern soft diets reduce vigorous chewing requirements, potentially weakening jaw muscles and limiting natural growth stimulation.
Oral Habit Correction: Addressing prolonged thumb sucking, pacifier use, and mouth breathing patterns that negatively impact jaw shape and dental alignment.
Postural Awareness: Poor posture influences head and jaw positioning, further affecting facial growth patterns.
By addressing these lifestyle factors, holistic orthodontics adopts a preventative, whole child approach that reduces the need for invasive treatments later in development.
Evidence Considerations and Professional Perspectives
While the functional principles underlying holistic orthodontic approaches are compelling, it remains essential to acknowledge that robust scientific evidence in some areas continues to develop. Many techniques including myofunctional therapy, functional appliances for airway development, and cranial osteopathy are supported by clinical experience, case studies, and smaller trials, but may lack the breadth of largescale, long-term randomised controlled trials that traditional orthodontics demands for widespread acceptance.
Consequently, holistic orthodontics often finds itself at the centre of professional debate. Critics argue that certain claims exceed current evidence, while advocates highlight gaps and limitations within conventional approaches that frequently ignore function and airway health considerations.
A balanced, evidence informed perspective remains essential. Holistic orthodontics should be viewed not as an alternative to scientific rigor, but as an evolving discipline that integrates clinical expertise with emerging research findings. The field benefits significantly from continued high quality studies to validate protocols, refine treatment guidelines, and bridge gaps between traditional and holistic models of care.
The Society for Dentofacial Growth and Function: Advancing Collaborative Care
Recognising the need for an integrative platform that brings together diverse expertise, the Society for Dentofacial Growth and Function (SDGF) was established in 2024. This organisation unites dentists, orthodontists, general medical practitioners, myofunctional therapists, osteopaths, ENT specialists, sleep medicine physicians, breathing specialists, allergists, lactation consultants, and other health professionals committed to advancing holistic, function focused care.
The SDGF’s mission focuses on significantly increasing paediatric health potential by promoting early screening and integrative treatment approaches to optimise children’s structural and functional development. The organisation aims to fully develop the structure and function of children’s airways, faces, and jaws while optimising oral functions including chewing, swallowing, speech, breathing, and sleep, alongside developing whole body biomechanics. By addressing these critical areas, the objective centres on improving future health outcomes across the general population.
The SDGF represents a unifying force in advancing more holistic, health focused orthodontic care through collaborative research, education, and clinical practice development.
Conclusion: Revolutionising Orthodontic Care for Future Generations
Holistic orthodontics represents a paradigm shift from reactive tooth straightening to proactive, health centred care. By focusing on airway development, nasal breathing optimisation, and functional harmony, clinicians can influence not only smile aesthetics but also overall health, sleep quality, and wellbeing of young patients.
Through early intervention, interdisciplinary collaboration, and commitment to understanding root causes of malocclusion, holistic orthodontics offers a comprehensive approach that supports children in reaching their full growth potential. Organisations such as the Society for Dentofacial Growth and Function are leading this movement, working to ensure that both form and function are prioritised in orthodontic care.
As scientific understanding continues to expand, the potential for holistic orthodontics to become a cornerstone of modern paediatric healthcare grows correspondingly. This comprehensive approach promises not just straighter teeth, but optimised breathing, improved sleep, enhanced facial development, and a foundation for lifelong health and wellness.
About the Author: Dr. Biju Krishnan is a dental practitioner with over 30 years of experience working with children and families, with a special interest in holistic orthodontic treatments. He is also a cofounder of the Society for Dentofacial Growth and Function (SDGF), a free to join organisation bringing together expertise and thought leadership in craniofacial development and function.
For more information about the SDGF or details on joining, please visit www.connectingheads.com